Cricket is not just a game. It is a complete science. Captains must know about the cricket fielding positions to get maximum benefit from the bowlers. The bowling side has to stop the batting side from making runs. In pursuit of it, the Bowling side places its ten fielders in different positions to stop the flow of runs. In the field, placing every inch and every yard matters. For instance, if the slip fielder is a yard deep, the catch will not carry to the fielder, so a formidable wicket chance is lost. Let’s Explain all the Cricket Fielding Positions.
Ground Distribution
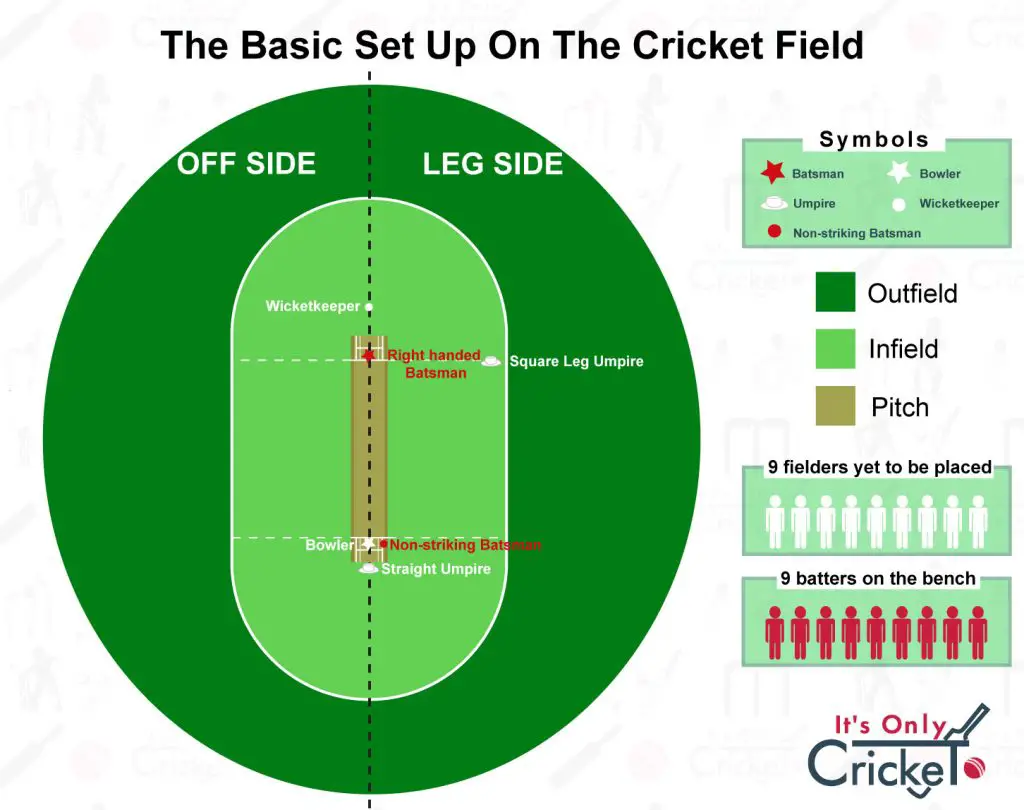
Cricket Ground is an area where Cricket Fielding Positions are applied. The cricket ground can be divided into three parts. The captain and even bowlers should be well aware of these dimensions to some extent.
Pitch
Onside or Legside
Offside
The pitch is where the main contest between the bowler and Batter occurs. The Right Side of the Pitch can be taken as Onside or legside. The left side then becomes offside (this is according to the Right-handed Batter).
PowerPlay Scenarios
There are many cricket fielding positions where fielders are placed, but as per the rules, there are some fielding restrictions, too. Regarding T20 Cricket, only two fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle in the powerplay. Two catching fielders must be placed inside the 30-yard circle. In ODI Cricket, there are three powerplays.
The First Powerplay Period lasts till the first ten overs. During overs 11-40, a maximum of four fielders can field outside the Inner circle. Up to 5 fielders can be placed outside a 30-yard circle during overs 41-50. There are no limitations regarding fielding in Test Cricket.
Cricket Fielding Positions

A knowledge of Cricket Fielding Positions and right-field placement makes a Captain successful. Recently, Babar Azam Resigned from Captaincy due to criticism of his Captaincy. So, knowing that fielding positions are important, here is a brief definition of every field position.
Wicket Keeper
The expert players can stand in these cricket fielding positions. The wicketkeeper is the player positioned right behind the Batter opposite the bowling end who catches the ball from the bowler without hitting the Batter or his bat.
Slips
The slips are positioned in an arc on the offside next to the wicketkeeper. In Swinging conditions, two and three slips are also taken to catch the ball in case of an edge from the Batter. Slips are crucial cricket fielding positions to get wickets with the new ball.
Gully
A gully is near the slips, slightly behind the wicket line on the offside. There is a much larger gap between slips and gully fielders as compared to the small gap between slips positions.
Third Man
On the offside, a third man can be positioned deep or short behind the wicket. The third man mostly stops the bowl when cover, gully, and slips fielders cannot stop it.
Point
A point fielder stands square to the wicket on the offside. The most active fielder of the team takes this position because batters often score runs through this area.
Mid Off
It is a relatively straight position close to the bowler on the offside. The Batter, who is known to play on the front foot, can hit the ball through this area to score runs.
Cover
It is one of the famous cricket fielding positions because many top players of the world, like Babar Azam, Virat Kohli, and Joe Root, are known for their cover drives. On the offside, it is positioned between point and mid-off. Many batters like to play cover drives, so fielders must stop the run flow by standing here.
Point Cover
It is a Fielding position where fielders are placed between Point and Cover. It is a small area, which is important to stop the runs from a batter who is strong on the off side. To control an inside-out drive, a fielder must stand here.
Extra Cover
The Fielding Position between Cover and Midoff is known as Extra Cover. A fielder is also placed as a deep extra cover to stop the boundary in the last few overs of the match.
Long Off
Long off is near the boundary, but the angle is the same as Mid Off. Batsmen often hit boundaries in this area during the death overs when bowlers tried to go full.
Mid On
In this position, the fielder will be relatively straight near the bowler but on the leg side. The batsman who can drive the ball well can score runs here.
Mid Wicket
Mid wickets is the halfway point between the bowler and wicketkeeper on the leg side. It is the most important position in the last few overs because most batters hit runs in this position.
Square Leg
The square Leg is a fielding position to the square on the onside. The fielders are positioned near the leg umpire.
Deep Square Leg
Deep Square league is again a crucial fielding point where the fielders have little time to react in these cricket fielding positions. The fielder must also know the angle of the ball because it can change after hitting the bat. The fielders are placed on the same dimensions as square legs but near the boundary.
Deep Midwicket
Deep Midwicket is known as one of the most important cricket fielding positions, as it covers the batsman’s hitting arc. It is located on the boundary at the same angle as Midwicket.
Long On
It is again among the toughest cricket fielding positions because many batters tend to go big on this side of the ground. This fielding position is mid-on but near the boundary on the leg side.
Fine Leg
Fine Leg is positioned at a 45-degree angle between the square Leg and the wicketkeeper on the leg side.
Deep Fine Leg
The deep fine Leg is the same as the dimension of the fine Leg but near the boundary.
Leg Slip
Sharp and active fielders are required to be placed in Slip cricket fielding positions. Leg slip is used as a catching position when bowlers bowl bouncers. For spinners, it is placed when bowls start to turn miles.
Short Leg
It is a close-catching position in front of the square on the leg side. The short-leg fielder is mostly used in test cricket but can also be used in ODI or T20 in pressure situations.
Silly Mid On
Silly mid-on is a close catching position in front of the square on the offside.

1 Comment
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It really helpful & it helped me out much. I am hoping to give one thing back and aid others such as you aided me.